For any business to achieve great success, its main goal is to enhance the competitive advantage of implementing expert systems. But, have you ever wanted to learn a new skill or gain more knowledge in a particular subject? That’s what Knowledge Acquisition is all about!
It’s the process of acquiring information and skills to become an expert in a specific area. It’s not just about gaining knowledge; it’s about internalizing that information so that you can apply it in real-world situations.
In short, Knowledge Acquisition is a valuable tool for personal and professional growth, allowing individuals to build new skills, solve complex problems, and make informed decisions.
Table of Content
What is Knowledge Acquisition?
Acquired knowledge is the one that organizations receive from external sources. External sources play a critical role in representing the full-scale view of the value chain for the organization. It involves the preparation of a knowledge map and encoding them into a knowledge base.
Implementing effective knowledge management systems and encouraging a culture of learning and collaboration can help organizations to improve their approach about knowledge acquisition processes.
What are these external sources then?
They are Customers, Suppliers, Competitors, and Partners/Alliances.
What are their primary roles in terms of the knowledge acquisition process?
Customers
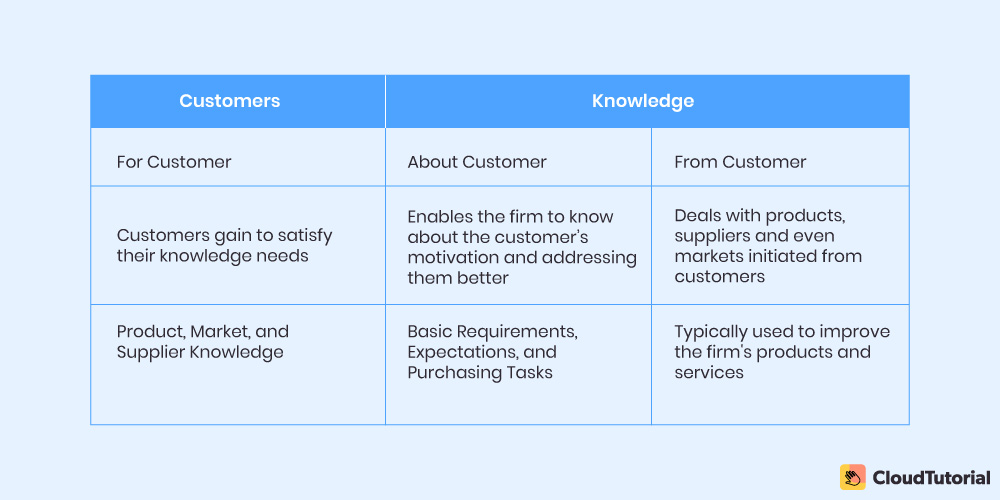
These three forms of knowledge for customers apply to the acquisition of knowledge and also to data or information. Further, the processing of such data can quickly be processed and used for the knowledge creation process and principles.
Knowledge sharing is an essential metric as it comes up with various forms based on business size. Knowledge Management plays a significant role in performing B2B relationships that, on one side, include the buyers to purchase more products.
On the other hand, the products can quickly be customized as per the customer’s need to a great extent using marketing knowledge.
Do you know what KM can do concerning knowledge sharing and acquisition?
- Feedback collection
- Analysis of marketing-related details
- Suggestion Collection
- Designing/Development Involvement
Suppliers
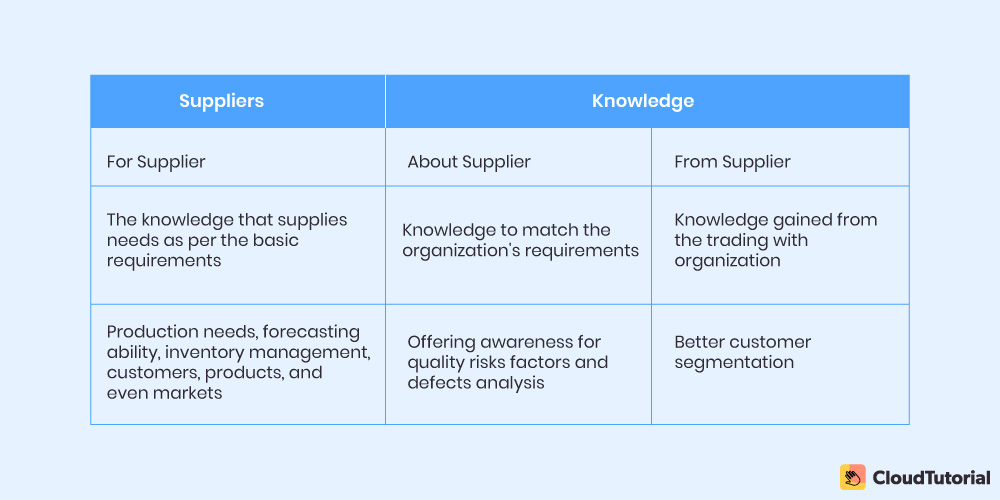
Acquisition of knowledge contain the data and information for suppliers that can quickly be processed and can perform as knowledge creation building blocks.
Competitors
It involves a simplistic approach by collecting, managing, and performing data, information, presentation, and knowledge transfer. Such details make it relatively easy for the customers to search, retrieve, and analyze it. For example- digital videos are an effective tool in this process as they provide visual and auditory answers to questions and boost problem-based learning.
Many such knowledge engineering approaches fall under the information management scope. Still, the main target is to opt for component usage with an appropriate decision-making ability to create a new level of knowledge or through critical knowledge transfer.
Partners/Alliance
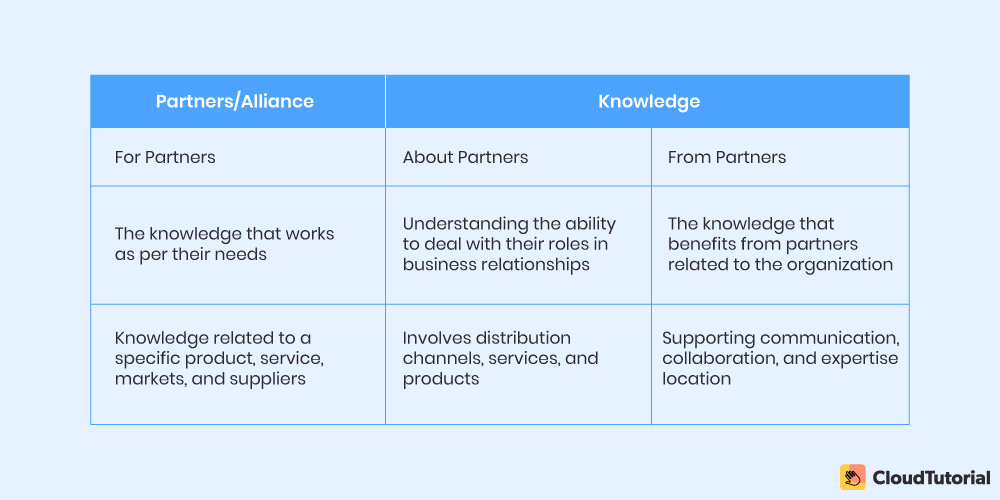
Proper and responsive management is mandated to identify valuable data resources as a potential benefit. One of the best recommendations is to deal with the two-way learning aspect: There is no specific end to the relationship, and your today’s partner can become your competitor tomorrow.

Looking For An Easier Knowledge Transfer Process?
CloudTutorial will make your knowledge transfer process easier than ever. Create SOPs, guides, and FAQs in clicks!
Characteristics of Knowledge Acquisition
The term “Knowledge Acquisition” helps the organization deal with the various thought processes between the employee and business on a large scale. On the other hand, semantic knowledge is crucial in the acquisition process as it enables individuals to make connections between new information and their existing knowledge base. However, there are essential characteristics that define knowledge acquisition:
Strong List of Questionnaires
With the combination of the various techniques, including conferences, it becomes quite possible to handle the list of questions that match the best as per the business requirements. Through these questions, an individual can find out the assessment results. These scores will be helpful for individual learning, and social learning, and also set goals for the future.
Decision Trees Methodology
For any knowledge engineer, the essential tools are the decision trees to deal with prototyping knowledge representations. In other words, they are of prime importance to knowledge acquisition, specifically on several different levels of artificial intelligence applications. The majority of the knowledge engineers came with the solution that experts show more interest in, usually relating to decision trees than rules.
Impressive Rule Development
The rules are the easiest way to utilize data characterizing during knowledge acquisition rather than opting to use complex representation methodologies. The most efficient pivotal point to redirect the knowledge acquisition course process is to apply the prototypic regulations on a large scale
During the interview process, the extra cases help the rule base expand on a large scale to deal with rule development. As a result, it helps provide an efficient way of feedback to structure the employees’ interviews
Theoretical Considerations
Human experts primarily use reasoning or pattern-recognition capabilities in building Expert Systems based on their particular knowledge and specialized intelligence. The expert system must be curious and possess a completely different classification concerning algorithms and database functionalities.
-
Domains
To determine whether an expert system suits the best for a specific problem domain, various features of the domain relate to knowledge acquisition.
- First, authentic experts, people possessing acknowledged expertise in the domain, must be available.
- Second, a general agreement among expert professionals about the precision of solutions in a domain should be available.
- Third, the knowledge engineer domain expert should quickly communicate with colleagues details of their problem-solving methods.
- Fourth, there should be narrow domain concepts with well-maintained solutions within the business network that do not require sense.
-
Experts
There are often various sources like books, guide manuals, advertisements, and simulation models; expert professionals use well-developed expert systems to a great extent.
The primary role of the expert professional when selecting a domain expert is not astonishing.
- First, an agreement must exist between the expert and the project’s goals.
- Second, better work cooperation for the expert and ease in working.
- Third, a domian expert must have impressive and effective verbal communication skills.
- Fourth, the expert’s commitment to the application to be on-time.
-
Knowledge Acquisition Technique
The interview is the heart of the process. The domain’s heuristic model extracts through a sequence of intense, well-ordered meetings that go through extension over many months.
Remember that expert professionals and knowledge engineers are not the same people. It is because the more profound the experts’ knowledge, the less they can describe their logic.
Moreover, the efforts to describe their process, expert professionals tend to justify their knowledge, leading to misleading factors.
The knowledge management methods include the general suggestions as mentioned below:
- Observation of an individual solving the obstacle
- Identification of data and process kind for solving the problem types using discussions
- Develop scenarios with the expert professional to associate with different project problem types or theories
- They possess an individual’s skills to resolve verbal mode problems and follow the essential steps of rational components
- Rules implementation to be defined for meetings and problem-solving capabilities on a large scale
Using expert systems requires a close working relationship between the knowledge engineer and the expert. Moreover, subsequent memory analysis is an important tool to evaluate the effectiveness of learning. Also, the Subsequent Memory GLM (General Linear Model) is a statistical approach to analyze the relationship between memory content and subsequent memory performance.

Want to Help Your Employees Find Information Quickly?
CloudTutorial makes it easy to find specific articles using categories and sub-categories options.
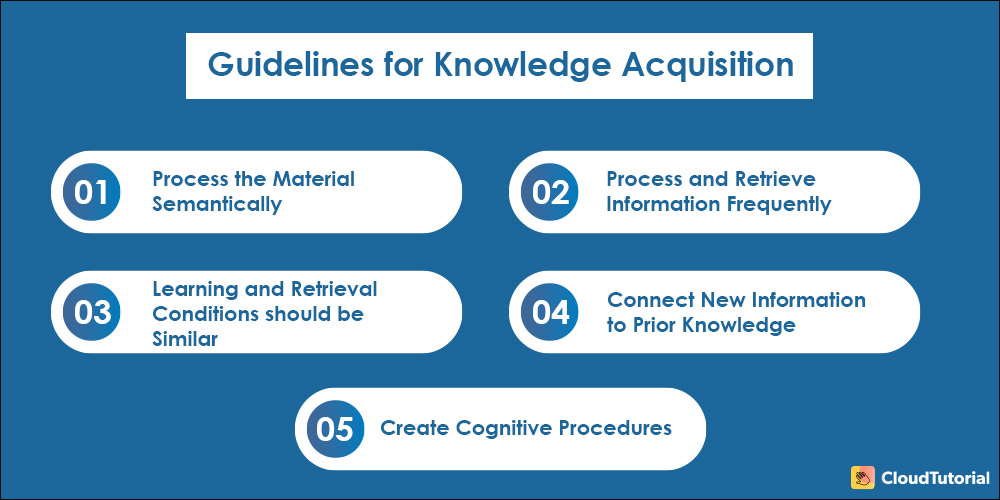
Guidelines for Knowledge Acquisition Process
Knowledge Management involves systematically collecting, organizing, and disseminating knowledge within an organization. Below are the five essential guidelines that help the organization deal with the knowledge acquisition process on a large scale.
-
Process the material semantically
The optimization of knowledge acquisition is mandatory to manage knowledge semantically. It becomes relatively easy for individuals or learners seeking to opt for individual learning through new material-based info. Semantic knowledge can be acquired through reading, discussion, and writing.
As per the research studies of Fergus Craik and Endel Tulving, the proof of importance for semantic processing came into existence. They came up with an idea where the participants can answer the questions correctly regarding the target words by merely following the depth of processing functionality. Confused? Let us take a simple example to explain it more clearly.
Consider the semantic question: Which of the following words fits the best as per the sentence: John met a _____ on the playground”? Friend or tree
This question invokes a detailed depth of processing that phonemic questions. Now, what is this phonemic? Which following rhymes with “late”? Crate or Tree
Moreover, the phonemic questions have greater depth than questions related to structure format. HOUSE or house – Which term is in capital letters?
From the above example mentioned above, the term processing activities using the semantic method is much better than using phonemically or structurally.
-
Process and Retrieve Information Frequently
The next learning objective is to perform testing and information retrieval multiple times. Now this reclaiming info, also known in other words, self-producing classification, can quickly be compared with just analyzing or copying it.
The research of the “generation effect” phenomenon or topic came into existence. It has taken decades to understand that the analyzing or copying approach takes less time or effort of memory than creating a new item or self-producing decision approach.
As the info reclining takes place, learning improvements exist just like academic functions deal with constant afterward or quizzes. Performing breaks up or distributing fetching strives to be the topmost factor.
-
Learning and Retrieval Conditions should be Similar
Generally, the knowledge representation of the knowledge works as per the relevant situations and internal and external context of the learning process. The info is perfect only when studying and retrieval are working in a in similar behavior.
For instance, consider the sentence: I like CHIP DIP. Here the participants include one adjective and one noun, and both are in capital letters. They are being informed that the noun memories will be performed afterward.
During the phase of the recognition test, participants are provided with a noun using:
- Original adjective: CHIP DIP
- With different adjective: SKINNY DIP
- Without adjective: DIP
In addition to it, to test accurate memory, the distinction of encoding is a vital part of any organization. Different questions tend to provide different understanding levels. The best examples recall data, typically dealing with varying levels of understanding, and unlike mental operations or theories, then information recognition tasks.
-
Connect New Information to Prior Knowledge
With the initiation of new material, adaptation knowledge retention exists that quickly links to proper and prior data that are interconnected to each other.
With prior adequate domain knowledge, the readers grab the advantages to fill contextual gaps that occur within the text. It eventually creates a better global understanding of the text.
To gain successful comprehension of the given text, prior knowledge is a must to make an accurate understanding of the text to a great extent.
-
Create Cognitive Procedures
Retaining and accessing procedural knowledge is relatively easy. It includes the relevant methods or shortcuts to complete a specific task and developing new memory strategies to enhance the distinct topic and retain critical knowledge.
Usually, multiple mnemonic categories exist to increase the data recall strategy, but the most popular references are the “method of loci.” Its primary purpose is to retain a long speech to get rid of using pen and paper.
Knowledge Acquisition is the process that is bounded by the following essential set of sources:
- Customers
- Suppliers
- Competitors
- Partners/Alliance
There are numerous ways to acquire knowledge. But acquiring rapidly changing or advancing knowledge, such as technology and science, is termed dynamic knowledge. Some of the best approaches to knowledge acquisition are:
- Research Meticulously
- Reading Books
- Operate Consciously
- Harness Productivity
- Complete Believe in Yourself
The four methods of acquiring knowledge is divided into four categories. Each category has its own strengths and weakness:
- Intuition
- Reading Books
- Authority
- Rationalism and Empricism
- The Scientific Method
To sum up, acquiring knowledge is an essential part of personal and professional development. Identifying a need, gathering knowledge (skills), and internalizing that knowledge through active engagement and a solid commitment to continuous learning are all parts of knowledge acquisition.
To keep learning successfully and improve your level of knowledge, it is important to revisit the information regularly and continue to expand your knowledge through additional electronic knowledge resources such as images, videos, and real-world applications.
Therefore, by embracing the learning process, people can advance greater levels of expertise and success in both their personal and professional life.

